

Threshold refers to the sensitivity of the gate. Common Noise Gate SettingsĪs one noise gate plug-in may look entirely different from that of another company, fear not! The controls are completely universal, whilst being intuitive for the user. Therefore, a noise gate can give the impression of a perfectly clean signal path, allowing your content and material to be the sole focus for the listener. This could be due to either a microphone, cable, or pre-amp. A noise gate can also be useful in removing a level of white noise, introduced in the recording path. Careful control of the parameters can result in a controlled and intimate signal path, ideal for dialogue. This can be in either the acoustic environment itself, such as a hum of an electronic device or a laptop fan.Īs recording locations may vary, a gate could even be put into use to control any unwanted subtle reverberate from the recording room. Why You Might use a GateĪ noise gate can be crucial in the removal of unwanted, low-level noise in a recording.
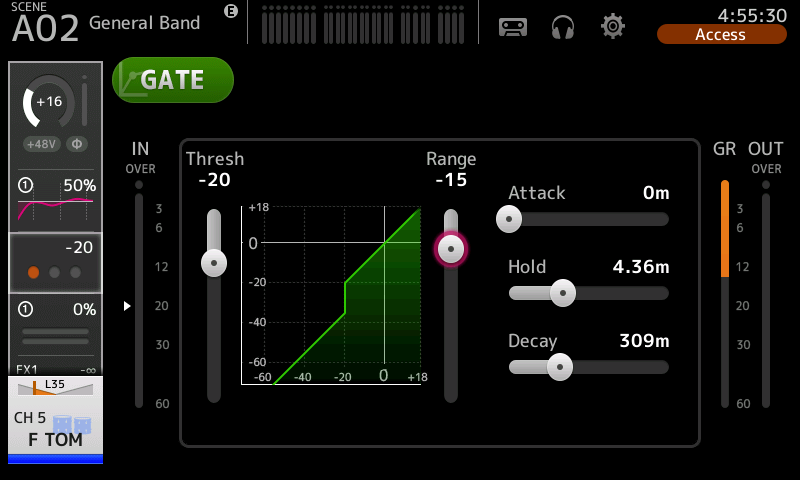
As with manual audio editing, pops and clicks can devalue a recording of any kind, so it is worth knowing where attack and release come into play. Noise gates are used best when they go unnoticed. The gate is only triggered (closed) when there is no signal above the set threshold.Ĭompressors, on the other hand, rely on a ratio, which dictates how much dynamic control the compressor performs once the threshold is passed. A gate will allow the intended signal through (open), without baring any effect on the result. They’re either open or closed, as with physical gates! This is crucial to understanding the difference between a gate and a compressor.

This can be perfect for getting rid of any computer fan noise, or other unwanted noises. A gate responds to an incoming signal, allowing anything above the desired dynamic threshold to be heard.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
